Magnesium, foil, thickness 0.0125 mm, size 25 x 25 mm, purity 99.9%. Magnesium, foil, thickness 0.0125 mm, size 50 x 50 mm, purity 99.9%. Magnesium, foil, thickness 0.015 mm, size 100 x 100 mm, purity 99.9%. Magnesium, foil, thickness 0.015 mm, size 25 x 25 mm, purity 99.9%. The atomic radius of Magnesium atom is 141pm (covalent radius).
The Element Magnesium
[Click for Isotope Data]
Atomic Number: 12
Atomic Weight: 24.305
Melting Point: 923 K (650°C or 1202°F)
Boiling Point: 1363 K (1090°C or 1994°F)
Density: 1.74 grams per cubic centimeter
Phase at Room Temperature: Solid
Element Classification: Metal

Period Number: 3
Group Number: 2
Group Name: Alkaline Earth Metal
What's in a name? For Magnesia, a district in the region of Thessaly, Greece.
Say what? Magnesium is pronounced as mag-NEE-zhi-em.

History and Uses:
What Block Is Magnesium In Chemistry
Although it is the eighth most abundant element in the universe and the seventh most abundant element in the earth's crust, magnesium is never found free in nature. Magnesium was first isolated by Sir Humphry Davy, an English chemist, through the electrolysis of a mixture of magnesium oxide (MgO) and mercuric oxide (HgO) in 1808. Today, magnesium can be extracted from the minerals dolomite (CaCO3·MgCO3) and carnallite (KCl·MgCl2·6H2O), but is most often obtained from seawater. Every cubic kilometer of seawater contains about 1.3 billion kilograms of magnesium (12 billion pounds per cubic mile).
Magnesium burns with a brilliant white light and is used in pyrotechnics, flares and photographic flashbulbs. Magnesium is the lightest metal that can be used to build things, although its use as a structural material is limited since it burns at relatively low temperatures. Magnesium is frequently alloyed with aluminum, which makes aluminum easier to roll, extrude and weld. Magnesium-aluminum alloys are used where strong, lightweight materials are required, such as in airplanes, missiles and rockets. Cameras, horseshoes, baseball catchers' masks and snowshoes are other items that are made from magnesium alloys.
Magnesium oxide (MgO), also known as magnesia, is the second most abundant compound in the earth's crust. Magnesium oxide is used in some antacids, in making crucibles and insulating materials, in refining some metals from their ores and in some types of cements. When combined with water (H2O), magnesia forms magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2), better known as milk of magnesia, which is commonly used as an antacid and as a laxative.
Hydrated magnesium sulphate (MgSO4·7H2O), better known as Epsom salt, was discovered in 1618 by a farmer in Epsom, England, when his cows refused to drink the water from a certain mineral well. He tasted the water and found that it tasted very bitter. He also noticed that it helped heal scratches and rashes on his skin. Epsom salt is still used today to treat minor skin abrasions.
Other magnesium compounds include magnesium carbonate (MgCO3) and magnesium fluoride (MgF2). Magnesium carbonate is used to make some types of paints and inks and is added to table salt to prevent caking. A thin film of magnesium fluoride is applied to optical lenses to help reduce glare and reflections.
Estimated Crustal Abundance: 2.33×104 milligrams per kilogram
Estimated Oceanic Abundance: 1.29×103 milligrams per liter
Number of Stable Isotopes: 3 (View all isotope data)
Ionization Energy: 7.646 eV
Oxidation States: +2
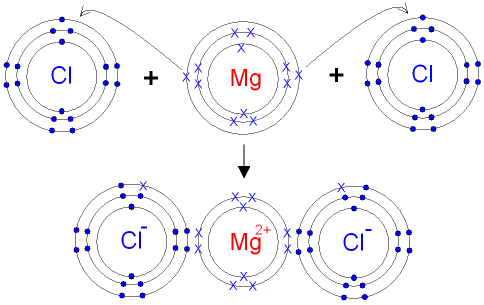
Electron Shell Configuration: | 1s2 |
2s2 2p6 | |
3s2 |
For questions about this page, please contact Steve Gagnon.
Generic Name: magnesium gluconate (mag NEE see um GLOO koe nate)
Brand Names: Mag-G, Magonate, Magonate Natal, Magtrate
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Sep 17, 2020.
What is magnesium?
Magnesium is a naturally occurring mineral. It is important for many systems in the body, especially the muscles and nerves.
Magnesium gluconate is used as a supplement to treat low levels or to maintain adequate levels of this mineral in the body.
Magnesium gluconate may also be used for purposes other than those listed in this medication guide.
Warnings
Before taking magnesium gluconate, tell your doctor if you are allergic to anything, or if you have have kidney disease. If you have any of these conditions, you may not be able to use magnesium gluconate, or you may need a dosage adjustment or special tests during treatment.Before using this medication, tell your doctor if you are pregnant or breast-feeding.
Before taking this medicine
Before taking magnesium gluconate, tell your doctor if you are allergic to anything, or if you have have kidney disease. If you have any of these conditions, you may not be able to use magnesium gluconate, or you may need a dosage adjustment or special tests during treatment. It is not known whether magnesium gluconate will harm an unborn baby. Do not take magnesium gluconate without telling your doctor if you are pregnant plan to become pregnant during treatment. It is not known whether magnesium gluconate passes into breast milk or if it could harm a nursing baby. Do not take magnesium gluconate without telling your doctor if you are breast-feeding a baby.How should I take magnesium?
Use this medication exactly as directed on the label, or as it has been prescribed by your doctor. Do not use the medication in larger amounts, or use it for longer than recommended.
Take this medication with a full glass of water. To help your body to better absorb magnesium gluconate, take the medication with a meal or just after eating.Measure the liquid form of magnesium gluconate with a special dose-measuring spoon or cup, not a regular table spoon. If you do not have a dose-measuring device, ask your pharmacist for one.
Store magnesium gluconate at room temperature away from moisture, heat, and light.What happens if I miss a dose?
Take the missed dose as soon as you remember. If it is almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and take the medicine at the next regularly scheduled time. Do not take extra medicine to make up the missed dose.
What happens if I overdose?
Seek emergency medical attention if you think you have used too much of this medicine.Symptoms of a magnesium gluconate overdose may include flushing, a slow heartbeat, severe drowsiness, confusion, muscle weakness, feeling light-headed, or fainting.
What should I avoid?
There are no restrictions on food, beverages, or activity while using magnesium gluconate unless your doctor has told you otherwise.
Magnesium side effects
Get emergency medical help if you have any of these signs of an allergic reaction: hives; difficulty breathing; swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat. Stop using magnesium gluconate and call your doctor at once if you have any of these serious side effects:nausea or vomiting;
fast or slow heart rate;
feeling light-headed, fainting; or
warmth, tingling, or redness under your skin.
Continue taking magnesium gluconate and talk to your doctor if you have any of these less serious side effects:
diarrhea;
bloating, gas; or
upset stomach.
Side effects other than those listed here may also occur. Talk to your doctor about any side effect that seems unusual or that is especially bothersome.
What other drugs will affect magnesium?
Certain antibiotics should not be taken at the same time as magnesium gluconate because they may not be absorbed as well by your body. If you are taking an antibiotic, avoid taking it within 2 hours before or after you take magnesium gluconate.
Before taking magnesium gluconate, tell your doctor if you are using any of the following drugs:
naladixic acid (NegGram);
penicillamine (Cuprimine, Depen);
an antibiotic such as tetracycline (Brodspec, Sumycin, Tetracap, and others), demeclocycline (Declomycin), doxycycline (Vibramycin, Monodox, Doryx, Doxy, and others), or minocycline (Minocin, Dynacin, and others);
a fluoroquinolone antibiotic such as ciprofloxacin (Cipro), gatifloxacin (Tequin), levofloxacin (Levaquin), lomefloxacin (Maxaquin), moxifloxacin (Avelox), norfloxacin (Noroxin), ofloxacin (Floxin), sparfloxacin (Zagam), or trovafloxacin (Trovan); or
a medication for osteoporosis or Paget's disease, such as alendronate (Fosamax), etidronate (Didronel), ibandronate (Boniva), risedronate (Actonel), or tiludronate (Skelid).
If you are using any of these drugs, you may not be able to use magnesium gluconate, or you may need dosage adjustments or special tests during treatment.
There may be other drugs not listed that can affect magnesium gluconate. Tell your doctor about all the prescription and over-the-counter medications you use. This includes vitamins, minerals, herbal products, and drugs prescribed by other doctors. Do not start using a new medication without telling your doctor.
Further information
- Your pharmacist has information about magnesium gluconate written for health professionals that you may read.
Magnesium Atom Bohr
- Consultation with a licensed health care professional is advisable before using any herbal/health supplement. Remember, keep this and all other prescription drug products, over-the-counter drug products, and herbal/health supplements out of the reach of children.
- Every effort has been made to ensure that the information provided by Cerner Multum, Inc. ('Multum') is accurate, up-to-date, and complete, but no guarantee is made to that effect. Drug information contained herein may be time sensitive. Multum information has been compiled for use by healthcare practitioners and consumers in the United States and therefore Multum does not warrant that uses outside of the United States are appropriate, unless specifically indicated otherwise. Multum's drug information does not endorse drugs, diagnose patients or recommend therapy. Multum's drug information is an informational resource designed to assist licensed healthcare practitioners in caring for their patients and/or to serve consumers viewing this service as a supplement to, and not a substitute for, the expertise, skill, knowledge and judgment of healthcare practitioners. The absence of a warning for a given drug or drug combination in no way should be construed to indicate that the drug or drug combination is safe, effective or appropriate for any given patient. Multum does not assume any responsibility for any aspect of healthcare administered with the aid of information Multum provides. The information contained herein is not intended to cover all possible uses, directions, precautions, warnings, drug interactions, allergic reactions, or adverse effects. If you have questions about the drugs you are taking, check with your doctor, nurse or pharmacist.
More about magnesium gluconate
Magnesium Atomic Number
Professional resources

Magnesium Atoms
Related treatment guides
Picture Of Magnesium Atom
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
